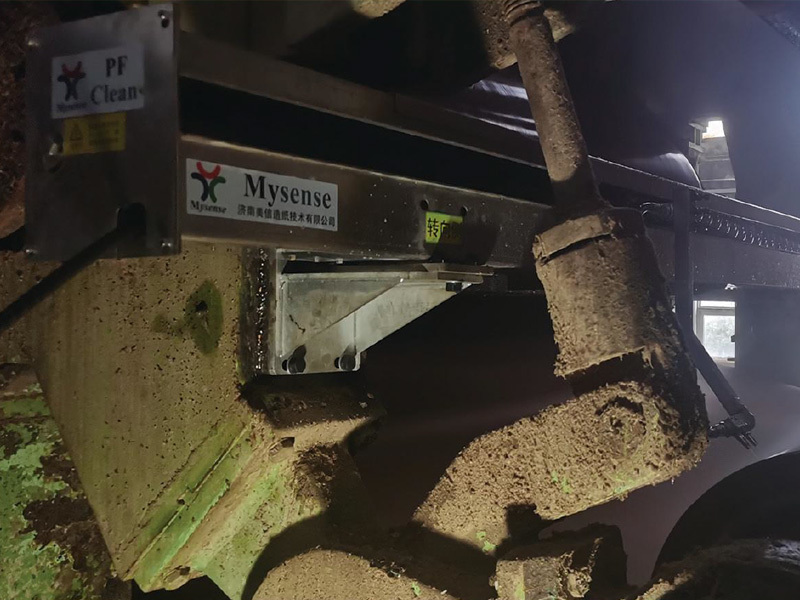
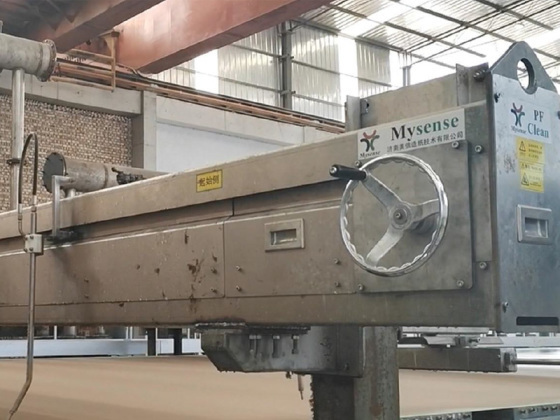
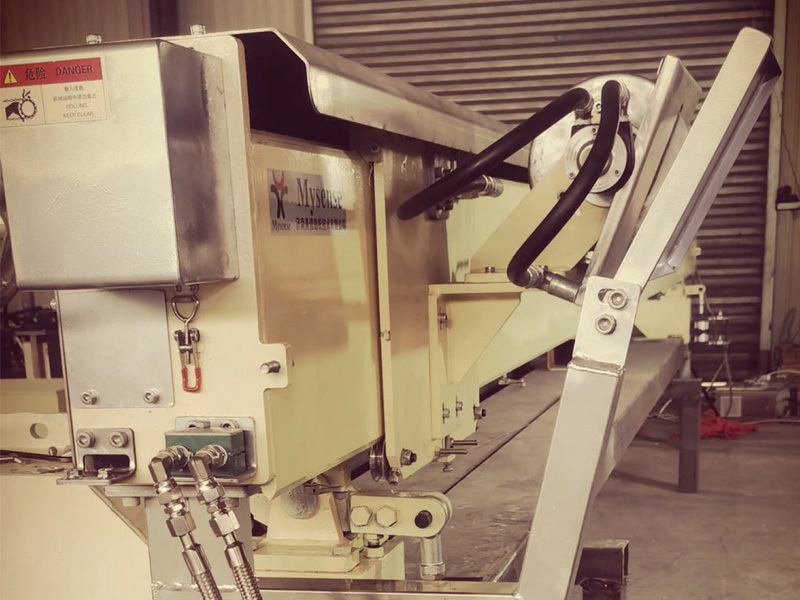
Mastering Tail Cutter Techniques: Advanced Strategies for Optimizing Wet Section Processes
Published on:
2025-04-30 10:20
Tail Cutter Mastery: Optimizing Wet Section Processes
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Tail Cutter Techniques
- Understanding Wet Section Processes in Manufacturing
- The Importance of Tail Cutters in Manufacturing
- Advanced Tail Cutter Techniques for Improved Efficiency
- Optimizing Wet Section Workflows with Tail Cutters
- Troubleshooting Common Issues in Wet Section Processes
- Case Studies and Success Stories in Tail Cutter Optimization
- Future Trends in Tail Cutter Techniques and Wet Section Processes
- Conclusion: Mastering Tail Cutters for Competitive Advantage
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Tail Cutter Techniques
In the realm of manufacturing, **tail cutters** play an indispensable role, particularly in the **wet section processes** of various industries. The mastery of tail cutter techniques can significantly influence the quality and efficiency of production lines, especially where precision cuts and material handling are critical. In this article, we will provide an in-depth exploration of how to optimize wet section processes through effective tail cutter strategies.
Understanding Wet Section Processes in Manufacturing
Wet section processes refer to a set of manufacturing operations that involve the manipulation of materials in a wet environment. This encompasses various sectors, including paper production, textile manufacturing, and certain applications in the electronics field.
The Role of Wet Section Processes
Wet section processes typically involve **water, adhesives, or other liquids** to facilitate cutting, bonding, or molding materials. Understanding the specific requirements of these processes is crucial for selecting the right tail cutter and optimizing its performance.
Key Components of Wet Section Processes
1. **Material Selection**: Different materials react uniquely under wet conditions, affecting the choice of tail cutter design and technique.
2. **Cutting Speed**: The speed at which the tail cutter operates can greatly influence the integrity of the cut and the overall efficiency of the process.
3. **Fluid Management**: Proper management of fluids used in wet section processes ensures optimal performance of tail cutters and minimizes waste.
The Importance of Tail Cutters in Manufacturing
Tail cutters are essential for achieving precise cuts in various manufacturing processes. Their importance can be categorized into several key areas:
Enhanced Precision and Quality
Utilizing advanced tail cutter techniques allows manufacturers to achieve higher precision levels in their cuts, which directly impacts the quality of the final product. A clean, precise cut reduces material waste and ensures that products meet stringent quality standards.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Optimizing tail cutter operations can lead to significant improvements in manufacturing efficiency. By streamlining the cutting process and reducing downtime, manufacturers can increase throughput and reduce costs.
Adaptability to Various Materials
Tail cutters can be designed to handle a wide range of materials, from soft textiles to hard composites. This versatility makes them invaluable in diverse manufacturing environments.
Advanced Tail Cutter Techniques for Improved Efficiency
To truly master tail cutter operations, manufacturers must employ advanced techniques that enhance both performance and productivity. Below are some of the most effective strategies:
1. Precision Calibration
Regular calibration of tail cutters ensures that they operate at peak efficiency. This includes adjusting the blade angle, cutting speed, and pressure applied during the cutting process.
2. Utilizing Smart Technology
Incorporating smart technologies such as sensors and automation can revolutionize tail cutter operations. By monitoring performance metrics in real time, manufacturers can make informed adjustments that optimize cutting efficiency.
3. Training and Skill Development
Investing in training programs for operators can lead to improved usage of tail cutters. Skilled operators can recognize issues early and implement corrective measures swiftly, reducing downtime.
4. Material-Specific Techniques
Different materials require unique cutting techniques. Tailor your approach based on the properties of the material being cut to achieve the best results.
5. Regular Maintenance and Upgrades
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule ensures that tail cutters remain in optimal condition. Upgrading to newer models with advanced features can also provide significant efficiency gains.
Optimizing Wet Section Workflows with Tail Cutters
Optimizing workflows in wet section processes involves integrating tail cutters effectively into the overall production line. Here are key considerations:
1. Workflow Analysis
Conducting a thorough analysis of existing workflows helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Focus on how tail cutters interact with other machinery and processes to streamline operations.
2. Integration with Other Equipment
Ensure that tail cutters are compatible with other equipment in the wet section process. This may require custom solutions or modifications to existing machinery to improve synergy.
3. Implementing Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing principles focus on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. Tailor your wet section processes to align with these principles, using tail cutters as a key component to achieve your goals.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Wet Section Processes
Even with the best practices in place, manufacturers may encounter challenges with tail cutters in wet section processes. Here are common issues and their solutions:
1. Blade Wear and Tear
**Wear and tear** is a common issue that can affect cutting performance. Regularly inspect blades for damage and replace them as needed to maintain cutting quality.
2. Material Jamming
Jamming can occur when material is not fed correctly into the tail cutter. Implementing proper feeding mechanisms can help alleviate this issue.
3. Inconsistent Cut Quality
If cuts are inconsistent, it may be due to incorrect calibration or material variability. Regularly recalibrating tail cutters and using consistent material batches can mitigate this problem.
Case Studies and Success Stories in Tail Cutter Optimization
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of optimized tail cutter operations. Here are a few success stories:
Case Study 1: Paper Production Efficiency
A leading paper manufacturer implemented advanced tail cutter techniques that resulted in a **20% reduction in material waste** and a **15% increase in production speed**. Regular training and smart technology integration were key components of their success.
Case Study 2: Textile Manufacturing Innovation
A textile company adopted a new tail cutter design that allowed for greater precision in cutting complex patterns. This innovation led to a **10% decrease in rejects** and improved overall product quality.
Future Trends in Tail Cutter Techniques and Wet Section Processes
As manufacturing technology evolves, so too will the techniques and tools used in wet section processes. Anticipated trends include:
1. Increased Automation
The use of automated systems to manage tail cutter operations will likely become more prevalent, driving efficiency and precision.
2. Advanced Materials
Emerging materials will require innovative cutting techniques, prompting manufacturers to continuously adapt their tail cutter strategies.
3. Sustainable Practices
Sustainability will play a critical role in the future of manufacturing, including the development of tail cutters that minimize waste and environmental impact.
Conclusion: Mastering Tail Cutters for Competitive Advantage
Mastering tail cutter techniques is vital for optimizing wet section processes in manufacturing. By implementing advanced strategies, focusing on precision, and continually adapting to new challenges, manufacturers can significantly enhance their efficiency, product quality, and competitiveness in the marketplace. Embracing innovation and ongoing education will ensure that your tail cutter operations remain at the forefront of manufacturing excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What materials can be effectively cut using tail cutters?
Tail cutters are versatile and can handle a range of materials, including textiles, paper, plastics, and composites.
2. How often should tail cutters be calibrated?
Regular calibration is recommended, ideally every production cycle or whenever there are noticeable changes in cutting performance.
3. What are the signs of blade wear?
Signs of blade wear include rough cut edges, increased friction, and unusual noises during operation. Regular inspections can help detect these issues early.
4. How can automation enhance tail cutter operations?
Automation can streamline the cutting process, reduce human error, and increase throughput by integrating real-time performance monitoring.
5. What is the impact of fluid management on tail cutter performance?
Effective fluid management ensures optimal cutting conditions, reduces material sticking, and enhances the overall performance of tail cutters in wet section processes.
Previous Article
Latest News